Binary Cycle of Geothermal Steam
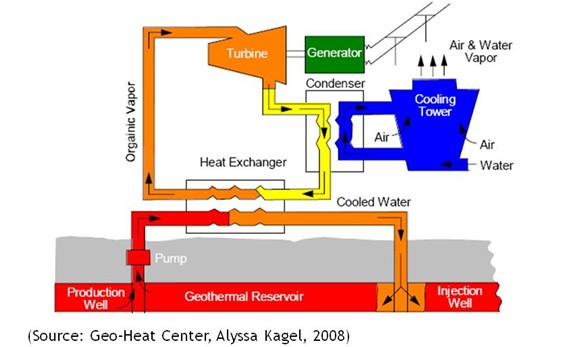
Binary cycle of geothermal plant is a very fascinating geothermal engineering which utilize the geothermal energy to the extent of zero withdrawal from underground. It is a kind of method which might be dreamed by people concerning the environmental issues, such as pollution, spill, and perhaps, the answer for renewable energy. Indeed, the geothermal energy itself is a clean energy that should be developed, but one special feature of the binary cycle is that the temperature of water in the reservoir doesn’t need to be as high as usual geothermal energy. Most of the time, the power plant for geothermal energy will need steam with temperature of 200 deg C, but by using this scheme, the reservoir fluid will only need as hot as 100-200 deg C. Among other renewable energy that can be used, perhaps geothermal energy should be considered more since the efficiency and technical knowledge are simply modifications of the system of petroleum production.
Looking at the picture (red->orange flow), we might see that the production well gain the fluid from geothermal reservoir, pumping it to the surface, thus the fluid will flow to the heat exchanger afterwards. One distinctive thing of geothermal from petroleum production is that the tools should be made by heat resistant materials. Also the pipes should be insulated to prevent the excessive heat loss. In heat exchanger, the geothermal heat will be transferred to the organic fluid in the other pipe. This is the main key of the binary cycle. The binary cycle uses the organic fluid whose boiling point is lower than water boiling point, so by using the heat provided by the water from geothermal reservoir, the organic fluid will change to vapor. This is the reason why this binary cycle is proper for medium temperature geothermal reservoir. When it is very hard to get the vapor from the water to go through the turbine, simply use this organic fluid instead. After flowing through heat exchanger, the water, which has been cooler, will flow to injection well. Sometimes, the injected formation will be drilled on lower elevation location, making the formation fluid flow naturally easier because of gravitation, thus needs less pumping power.
On the other system of heat exchanger (yellow-orange flow), the organic vapor will flow to the turbine. This turbine works from the energy of this organic vapor. There are spinning blades that turn when vapor blows past them. The turbine will turn electricity generators at incredibly high speed. This is another superiority of geothermal energy than other renewable energies: that the steam turbine rotates at 1800–3600 rpm, which is 100-200 times faster than typical wind turbine. Also, about the turbine, we may see another advantageous reason to use the low boiling point organic fluid instead of water in medium temperature geothermal reservoir. Water induction into steam turbines may create bunch of problems, Even a small amount of water may lead to huge damage on the turbine blades, the cylinders, and the housing. The turbine will make the generator produce electricity, and the electricity can be used by people afterwards.
After the turbine, the organic vapor will flow through the condenser. Condenser is another “heat exchanger”, which is used to exchange the heat from the organic fluid flowing from turbine and the water from cooling tower. But that is not the main function. The purpose of the condenser is to create the vacuum pressure (lower than atmospheric pressure). As we know, vapor will consume more extensive volume than liquid. When the heat exchange happened between vapor and water from cooling tower, the vapor will condense, thus decreasing in volume. Since the volume decreased, the condenser will have less pressure. This vacuum pressure in condenser is very important to make the energy transfer in the turbine become efficient, since the energy transfer in the turbine is related to the pressure difference of inlet and outlet of the turbine. In this binary cycle, the surface condenser, in which the vapor does not directly contact the cooling fluid, should be used. The cooling water itself should be obtained by water sources near the site, might be rivers or lake. Most of the time, these sources do not provide enough water to absorb all the heat. More common method is by utilizing cooling tower, either mechanical draft cooling water, in which the heat transferred to the air induced by fans; or natural draught cooling water, in which the heat transferred to the air induced by the shape and height of cooling tower.
The organic fluid then flow to the heat exchanger to gain heat from the formation water again and the cycle continues. It might be seen that both the formation fluid and organic fluid cycles in a closed loop, thus we may conclude that this binary cycle of steam is very environment friendly energy. This method has been successfully applied in Parantuka, Kamchatka Peninsula, and Otake.
One noticeable problem has been observed on this method usage is that the implementation should be done on medium temperature reservoirs instead of the high temperature one, since further intensive assessment on the heat resistance of organic vapor and heat exchanger should be done on the high temperature reservoirs.
Do you love this post? Thank you! I feel appreciated. This post is under the category of Petroleum Engineering, you may love to see other similar posts HERE
Do you love this post? Thank you! I feel appreciated. This post is under the category of Petroleum Engineering, you may love to see other similar posts HERE
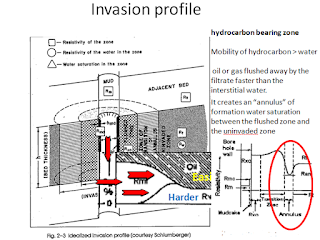
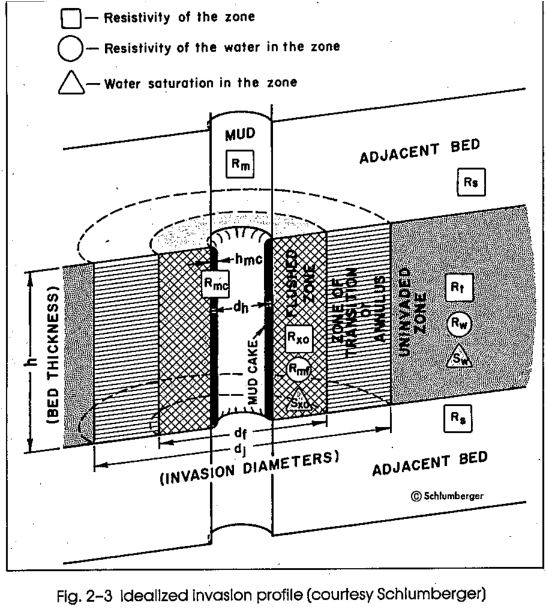

Comments
Post a Comment